Table of Contents:
Understanding Gum Rosin Grades
3. WG (Water White Glass) Grade
Significance of Gum Rosin Specifications
Characteristics of High-Quality Gum Rosin Grades
Applications of Different Gum Rosin Grades
– Paints, Coatings, and Varnishes
Selecting the Right Gum Rosin Grade for Your Application
Quality Control and Testing of Gum Rosin Grades
Storage, Handling, and Transportation of Gum Rosin
Understanding Gum Rosin Grades
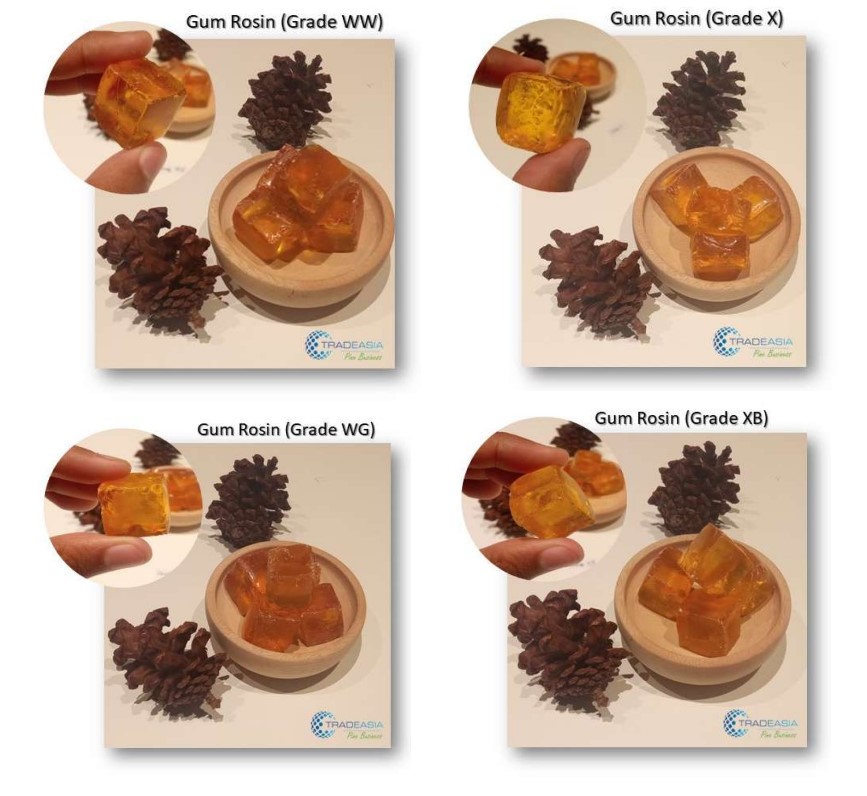
Gum rosin grades encompass various classifications and categories based on specific characteristics and properties, indicating the varying quality and suitability of gum rosin for different applications. These grades, such as WW, N, WG, X, and more, possess distinct attributes that render them appropriate for specific uses. Factors like color, transparency, softening point, acid value, and viscosity are often employed in the classification of gum rosin grades, enabling manufacturers and consumers to make well-informed choices. Multiple factors, including pine tree species, geographical region, extraction methods, processing techniques, and purification processes, can influence gum rosin grades, necessitating an understanding of these elements to grasp the variations in gum rosin quality.1. WW (Window Glass) Grade
- WW grade gum rosin is characterized by its pale yellow to amber color.
- It has high transparency and is commonly used in applications where color stability is important, such as in the production of light-colored adhesives, varnishes, and coatings.
- WW grade gum rosin typically has a moderate softening point and good resistance to oxidation.
2. N (Non-crystallized) Grade
- N grade gum rosin is derived from partially or fully hydrogenated gum rosin.
- It does not exhibit the crystalline structure commonly found in other grades.
- N grade gum rosin has a higher softening point compared to other grades, making it suitable for applications that require heat resistance or increased durability.
3. WG (Water White Glass) Grade
- WG grade gum rosin is highly refined to achieve exceptional color clarity and transparency.
- It has a water-white appearance and is virtually free from impurities.
- WG grade gum rosin is primarily used in applications where absolute clarity and color stability are critical, such as in the production of transparent adhesives, varnishes, and inks.
4. X (Extra Pale) Grade
- X grade gum rosin is known for its extremely light color and high transparency.
- It is produced through a rigorous refining process to minimize impurities and achieve excellent color stability.
- X grade gum rosin is commonly used in applications that require high-quality, light-colored formulations, such as in cosmetics, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
5. M (Medium) Grade
- M grade gum rosin falls between the WW and N grades in terms of color and softening point.
- It has a moderate yellow color and a relatively lower softening point compared to WW grade.
- M grade gum rosin finds applications in a wide range of industries, including adhesives, sealants, inks, and coatings.
6. K (Kondakova) Grade
- K grade gum rosin is produced from a specific variety of pine trees found in Russia.
- It is characterized by its high acid value and unique aromatic properties.
- K grade gum rosin is commonly used in the production of varnishes, paints, and adhesives, particularly in Russia and Eastern Europe.
Significance of Gum Rosin Specifications
Specifications are essential for ensuring the quality and consistency of gum rosin by defining desired values for attributes such as color, softening point, acid value, and impurity levels. They serve as benchmarks for quality control, maintaining consistent performance across various applications. Additionally, gum rosin specifications facilitate compliance with regulatory standards by setting limits for contaminants and impurities, ensuring product safety and adherence. Different industries have specific requirements for gum rosin specifications, such as prioritizing tackiness and bond strength in the adhesive industry or emphasizing color stability and pigment compatibility in the paint industry. It is crucial to understand these industry-specific needs when selecting gum rosin grades.
Characteristics of High-Quality Gum Rosin Grades
Transparency and Color
High-quality gum rosin grades generally exhibit excellent transparency and color characteristics. They have a clear and bright appearance, indicating purity and minimal impurities. Transparent gum rosin is often preferred in applications where color stability is essential, such as in the production of light-colored adhesives or coatings.
Softening Point
The softening point refers to the temperature at which gum rosin softens and becomes tacky. High-quality gum rosin grades typically have a well-defined and consistent softening point, ensuring predictable performance during processing and application. A specific softening point range is preferred based on the intended use of the gum rosin.
Acid Value
The acid value of gum rosin is a measure of its acidity, indicating the amount of free acid present in the resin. High-quality grades tend to have lower acid values, signifying lower acidity and better stability in formulations. A lower acid value is often desirable in applications where the gum rosin interacts with alkaline substances or metals.
Solubility
Gum rosin grades should exhibit appropriate solubility or insolubility characteristics depending on the intended application. Insoluble gum rosin is preferred in applications where long-term stability, resistance to moisture, or compatibility with other materials is required.
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a liquid or semi-solid substance to flow. Different gum rosin grades may possess varying viscosities, which can impact their processability and application methods. High-quality gum rosin grades usually exhibit consistent viscosity characteristics that facilitate ease of handling and formulation.
Other Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Apart from the aforementioned characteristics, high-quality gum rosin grades may possess additional desirable properties, such as low odor, minimal content of volatile compounds, and good thermal stability. These attributes contribute to the overall quality and performance of gum rosin-based products.

Applications of Different Gum Rosin Grade
– Adhesives and Sealants
Gum rosin finds extensive use in the adhesive and sealant industry, where they act as an essential component in formulating various adhesive types. Different grades are selected based on factors such as tackiness, bond strength, compatibility with other ingredients, and the specific requirements of the intended substrate.
– Paints, Coatings, and Varnishes
Gum rosin is widely utilized in paints, coatings, and varnishes, contributing to their adhesion, gloss, and film-forming properties. The selection of grades depends on factors such as solubility, compatibility with pigments, drying time, and desired film characteristics.
– Inks and Dyes
In the ink and dye industry, gum rosin serves as binders and rheology modifiers, providing adhesion, color stability, and viscosity control. The choice of gum rosin grade depends on the ink formulation, printing process, desired print quality, and substrate compatibility.
– Rubber Industry
Certain gum rosin grades are utilized in the rubber industry to improve the tackiness, bonding properties, and processability of rubber compounds. They enhance the adhesion of rubber to various substrates and contribute to the overall performance of rubber products.
– Paper and Packaging
Gum rosin is incorporated into paper and packaging formulations to improve strength, water resistance, printability, and surface properties. The selection of the appropriate grade depends on the specific paper or packaging application, including factors such as compatibility with other additives and desired performance attributes.
– Other Industries
Gum rosin also finds applications in industries such as personal care products, construction materials, electrical insulations, and more. Each industry has its unique requirements and specifications for gum rosin grades, making the selection process crucial for achieving desired outcomes.
Selecting the Right Gum Rosin Grade for Your Application
When choosing a gum rosin grade, it is crucial to understand the specific requirements of your application, considering factors such as desired properties, compatibility with other ingredients, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards. Evaluate the compatibility of various gum rosin grades with your formulation’s ingredients to avoid performance or stability issues. Assess the necessary performance attributes, such as adhesion strength, color stability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or weathering, and select a gum rosin grade that meets these requirements. Additionally, consider the cost and availability of different grades, balancing quality and accessibility. To make an informed decision, request samples from reputable suppliers and conduct thorough testing in your specific application or formulation to evaluate performance, compatibility, and suitability.
Quality Control and Testing of Gum Rosin Grades
Industry Standards and Testing Methods
Quality control of gum rosin grades involves adherence to industry standards and specifications. Familiarize yourself with the relevant standards and testing methods established by industry organizations, ensuring consistency, reliability, and comparability of the gum rosin products.
Certifications and Compliance
Verify that the gum rosin supplier follows quality management systems and holds certifications or accreditations that validate their commitment to producing consistent, high-quality gum rosin grades. Compliance with regulatory requirements is also crucial, especially for applications subject to specific regulations or safety standards.
Assessing Gum Rosin Quality and Purity
Conduct rigorous quality control checks to assess the purity and quality of gum rosin grades. This may involve testing for impurities, acid value, softening point, color, and other physical or chemical characteristics. Utilize appropriate analytical techniques and equipment for accurate and reliable results.
Laboratory Analysis and Quality Assurance
Establish a robust quality assurance program within your organization or work with certified laboratories to analyze and verify the quality of gum rosin grades. Regular testing and analysis ensure consistent product quality, allowing you to meet customer expectations and maintain a competitive edge.
Storage, Handling, and Transportation of Gum Rosin
Proper Storage Conditions
Gum rosin should be stored in suitable conditions to maintain its quality and prevent degradation. Store gum rosins in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or ignition. Proper packaging and labeling are essential to minimize the risk of contamination or damage.
Packaging and Container Considerations
Ensure that the packaging and containers used for gum rosin storage are appropriate for the grade and quantity being stored. Use containers that provide adequate protection against moisture, physical damage, and contamination. Follow safety guidelines and regulations for packaging and labeling.
Safety Precautions and Handling Guidelines
Adhere to safety precautions when handling gum rosin. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses to minimize direct contact. Follow handling guidelines provided by the supplier to prevent accidents, spills, or exposure to hazardous conditions.
Transportation Best Practices
When transporting gum rosin, ensure compliance with applicable regulations and guidelines for hazardous materials transportation, if applicable. Use appropriate packaging, labeling, and securement methods to prevent leaks, spills, or damage during transit. Follow local, national, and international regulations regarding the transportation of gum rosin.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Contamination and ImpuritiesContamination or impurities in gum rosin can affect its performance and cause compatibility issues with other ingredients. Regularly inspect and test incoming gum rosin shipments for impurities, and establish quality control measures to minimize contamination risks.
Shelf Life and Storage Issues
Improper storage conditions or extended storage durations can lead to degradation or changes in gum rosin properties. Follow recommended storage guidelines, monitor shelf life, and conduct periodic quality checks to ensure the stored gum rosin remains usable and within specification.
Handling and Processing Difficulties
Certain gum rosin grades may present challenges during handling, processing, or formulation due to their physical properties or characteristics. Explore techniques or additives that can facilitate easier handling or processing, and consult with experts or suppliers for troubleshooting assistance.
Compatibility Problems
Compatibility issues may arise when using gum rosin grades in combination with other ingredients or additives. If compatibility problems occur, assess the formulation components, consult with experts, and consider alternative gum rosin grades or adjustments to the formulation to achieve the desired compatibility and performance.
Industry Trends and Innovations in Gum Rosin Grades
The industry is experiencing a shift towards sustainable sourcing practices for gum rosin, driven by increasing environmental awareness. This shift involves responsible forestry management, traceability, and minimizing the environmental impact during extraction and processing. Additionally, there is a growing exploration of alternative gum rosin sources through the development of bio-based and renewable materials. Researchers and manufacturers are investigating options like bio-based resins, modified rosin derivatives, and renewable feedstocks to reduce dependence on traditional gum rosin grades. Moreover, ongoing innovations aim to modify gum rosin properties through processes like esterification, hydrogenation, or resin blending, resulting in improved characteristics, compatibility, and functionality for specific applications.
In conclusion, understanding gum rosin grades and specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate grade for your specific application. Consider the characteristics, performance requirements, and industry standards to make informed decisions. Implement robust quality control measures, adhere to proper storage and handling practices, and stay updated on industry trends and advancements. By doing so, you can effectively harness the benefits of gum rosin and ensure optimal performance in your products or formulations.