Introduction
Gum rosin, a natural resin derived from pine trees, has been an essential material with a wide array of applications across industries. From adhesives to fine arts, its versatile properties make it a sought-after ingredient in various products. However, not all gum rosin is created equal. Different sources and extraction methods yield unique variations in their properties and applications. In this article, we will delve into the comparison of gum rosin from different sources, exploring the distinct qualities they possess and their potential implications in various fields.
Understanding Gum Rosin and Its Production
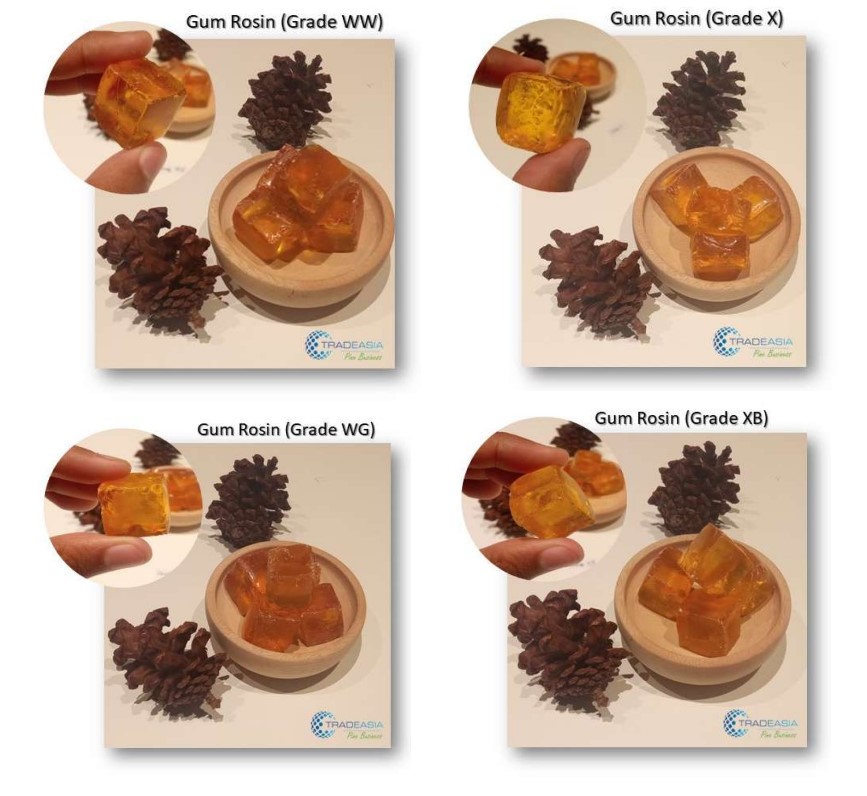
Before diving into the comparison, let’s briefly understand what gum rosin is and how it is produced. Gum rosin is a natural resin obtained from the sap of pine trees, primarily Pinus spp. Its extraction process involves tapping into the tree, collecting the resin, and then processing it through heat and distillation to obtain the final product. The final form of gum rosin can vary in color, transparency, and chemical composition depending on the tree species and regional factors.
Comparing Sources of Gum Rosin
Chinese Gum Rosin (Pinus massoniana)
Source: Chinese gum rosin is obtained from the sap of Pinus massoniana, commonly known as the Masson pine or Chinese red pine. This species is widely distributed in southern China and neighboring regions.
Properties: Chinese gum rosin is prized for its light color, ranging from pale yellow to almost transparent. Its transparency makes it an ideal choice for applications where aesthetics and clarity are important. The rosin has a relatively high melting point, which contributes to its stability in various industrial processes.
Applications: Chinese gum rosin is extensively used in the adhesive industry, where it imparts good tackiness and bonding properties. It is also popular in the manufacturing of coatings, varnishes, and printing inks. The stability and consistent quality of Chinese gum rosin make it a preferred choice in a wide range of applications.
Brazilian Gum Rosin (Pinus elliottii)
Source: Brazilian gum rosin is derived from the resin of Pinus elliottii, commonly known as slash pine. This species is native to the southeastern United States but is also widely cultivated in Brazil and other parts of South America.
Properties: Brazilian gum rosin exhibits a slightly darker color compared to its Chinese counterpart. It possesses moderate transparency and a lower melting point, which affects its overall consistency and handling characteristics.
Applications: Brazilian gum rosin finds application in adhesives, varnishes, and inks. Its unique properties make it suitable for use in specialty adhesives, such as those used in the production of chewing gum. The rosin’s properties make it well-suited for products where moderate tackiness and adhesive strength are desired.
Indonesian Gum Rosin (Pinus merkusii)
Source: Indonesian gum rosin is obtained from the resin of Pinus merkusii, commonly known as Merkus pine. This species is native to Indonesia and other Southeast Asian countries.
Properties: Indonesian gum rosin is recognized for its darker color and lower transparency compared to Chinese and Brazilian gum rosins. It has a relatively higher acid number, indicating a higher content of acidic components.
Applications: Indonesian gum rosin is widely used in the soap-making industry due to its ability to enhance lathering properties in soap formulations. It acts as a stabilizer and contributes to the overall structure of the soap. Additionally, it finds applications in cosmetics and personal care products, where its unique properties play a vital role in enhancing product performance.
American Gum Rosin (Pinus taeda)
Source: American gum rosin is obtained from the resin of Pinus taeda, commonly known as loblolly pine or North American pitch pine. This species is native to the southeastern United States.
Properties: American gum rosin is characterized by its amber color and excellent transparency. It has a relatively low acid number, indicating a lower content of acidic components compared to Indonesian gum rosin.
Applications: American gum rosin is widely used in the paper and printing industry, where it serves as a critical component in paper sizing to improve water resistance and ink holdout. It is also employed in the manufacturing of various printing inks due to its stable pigmentation properties. Moreover, American gum rosin is popular among artists for creating glossy varnishes and oil painting mediums in the field of fine arts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum rosin is a versatile and valuable natural resin that varies in properties based on its source. Chinese, Brazilian, Indonesian, and American gum rosins each offer unique characteristics, catering to specific industries and applications ranging from adhesives and sealants to fine arts and soap-making. Understanding these differences can help manufacturers and consumers alike make informed decisions when selecting the right type of gum rosin for their needs.
As technology and research continue to evolve, further insights into gum rosin’s properties and applications may emerge, opening new possibilities for this ancient and versatile natural material.